The widespread adoption of Wi-Fi® in hospitals in recent years has transformed healthcare – for the greater good. As a result of Wi-Fi, entirely new waves of medical devices are being created to take advantage of the mobile connectivity that Wi-Fi provides in healthcare facilities – wireless EKGs, infusion pumps, and blood pressure cuffs to name a few. Mobility in hospitals allows clinicians to provide accurate and timely patient monitoring and enables them to focus on providing the best quality of patient care, rather than on administrative tasks. The increasing numbers of wireless medical devices in hospitals has led to the ultimate goal: improved patient care.
Wi-Fi has changed the healthcare environment
Wi-Fi technology has changed how healthcare is conceptualized and delivered. This change has led to the idea of the Connected Hospital, a vision of a fully integrated hospital where wireless technology allows caregivers and patients to roam throughout the hospital while providing accurate, real-time monitoring. In the Connected Hospital, wireless technologies like Wi-Fi will fuel patient safety, data accuracy, and mobility. Within the Connected Hospital, nurses can monitor multiple patients remotely from one main station, receiving alerts and observing data captured on patients’ health in real-time. Doctors can make more informed decisions with accurate and up-to-date patient information, leading to better patient outcomes. In addition, patients and their families can feel safe knowing they will always receive the correct dosage of the right medication – resulting in overall better care from medical staff and a more comfortable environment free from wired devices. Mobile medical devices can even travel with patients so they can be monitored from the comfort of their own home.

Figure 1: A fully integrated hospital where wireless technology enables mobility while providing real-time monitoring.
Cutting the cord
Although Wi-Fi is widespread in healthcare facilities, cutting the cord for medical devices has been a slow process. Nevertheless, the opportunities for growth increasingly outweigh the challenges associated with transitioning to wireless medical devices. Naturally, security, privacy, and patient safety are paramount considerations, but the risks associated with wireless medical devices can be mitigated when the best solution is chosen and the appropriate steps to implement the technology are taken. When dealing with sensitive data, wireless medical devices must have adequate security, such as IEEE 802.11i. IEEE 802.11i provides strong encryption and authentication capabilities in the form of WPA2™-Personal and WPA-2 Enterprise. WPA2-Enterprise is better suited for a hospital setting due to its central management capabilities, which allow for easier authentication management. Click here to find out how security mechanisms impact mobility.
 |
Figure 2: Not all wireless medical devices have the same Wi-Fi mobility capabilities, so it is important that wireless medical devices that have embedded Wi-Fi modules that go through the roaming process quickly and seamlessly are chosen. |
In addition, not all wireless medical devices have the same Wi-Fi mobility capabilities, so it is important that hospital IT professionals choose wireless medical devices that have embedded Wi-Fi modules that go through the roaming process quickly and seamlessly. More information about how clients roam can be found here.
Incentives, documentation, and assistance exists in order for hospital IT staff to make informed decisions, as well as an entire community of medical device manufacturers, wireless module manufacturers, and infrastructure providers for IT professionals to look to for guidance and support. Wi-Fi Alliance has even developed a series of FAQs to assist IT administrators looking to learn more about the design and management of hospital Wi-Fi networks.
The adoption of wireless medical devices in hospitals can be fueled by following best practices and learning from the experiences and success stories of other hospitals. Once everyone is in accordance on how to create a secure and reliable network, hospitals can then take advantage of the secure wireless connectivity that Wi-Fi provides.
The statements and opinions by each Wi-Fi Alliance member and those providing comments are theirs alone, and do not reflect the opinions or views of Wi-Fi Alliance or any other member. Wi-Fi Alliance is not responsible for the accuracy of any of the information provided by any member in posting to or commenting on this blog. Concerns should be directed to info@wi-fi.org.
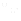



Add new comment